

August 11, 2023

2792 Views

5 min read
What is the ELD in Trucking?
Page Contents
The adoption of Electronic Logging Devices (ELDs) has seen a significant increase among truck drivers and carriers, becoming the new industry norm due to the federal government’s recent ELD mandate. For burgeoning businesses with a fleet of vehicles, it becomes crucial to have a comprehensive understanding of ELDs. Keep reading to learn about Electronic Logging Devices, their importance and benefits, how they work, compliance requirements, and more.
What is the ELD in Trucking?
Explanation of ELD (Electronic Logging Device)
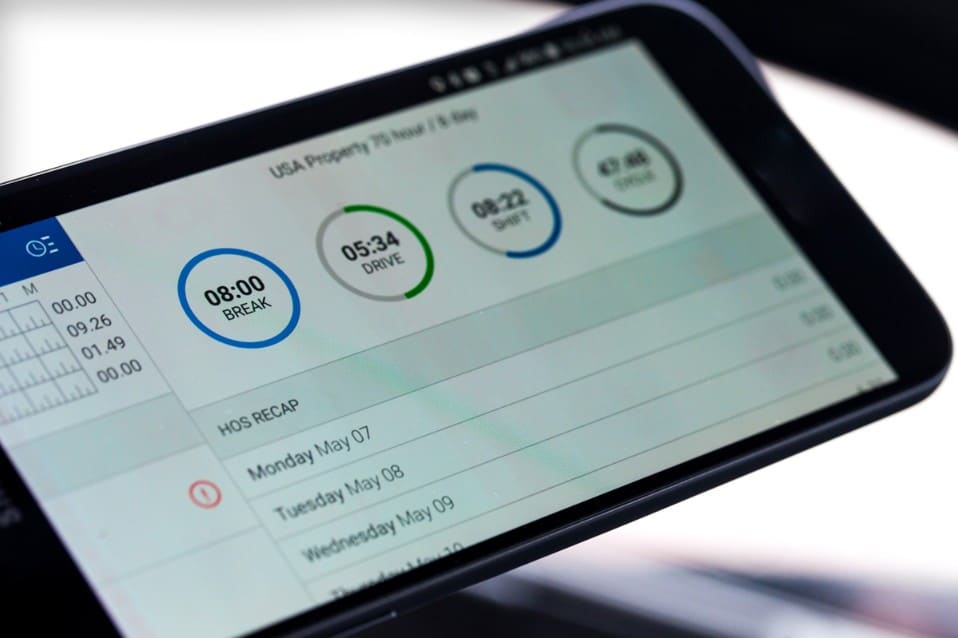
An electronic logging device (ELD) is used by individuals who operate commercial motor vehicles (CMVs). ELD automatically keeps track of the driving time records and hours of service (HOS). The ELD automatically captures essential information like the trucker’s location, ignition status, engine hours, and miles driven by directly syncing with the vehicle’s engine.
The primary purpose of the ELD is to provide real-time updates on a trucker’s status to both dispatchers and commercial drivers. This information ensures that both parties know the driver’s available hours and helps prevent violations of HOS requirements. With HOS information automatically recorded, compliance managers can generate reports, review HOS statuses, and plan routes to avoid situations where drivers might unintentionally mean to violate HOS regulations.
The ELD systems go beyond AOBRDs (automatic onboard recording devices), setting a new industry standard for commercial vehicles. They record everything your paper logs would and provide additional valuable information.
Importance and Benefits of ELD Implementation in Trucking
ELD devices play a crucial role in the trucking industry by ensuring accurate tracking of HOS compliance while eliminating the delays caused by paper logs. Some of the key benefits include:
Simplify Fleet Compliance
ELDs automatically track drivers’ driving time and maintain the Record of Duty Status (RODS). By recording and monitoring driving time and HOS compliance, ELDs provide accurate recording and enable efficient communication of data required for compliance reporting.
Streamline Operations
Replacing paperwork with digital data simplifies communication between drivers and fleet managers, reducing administrative burdens. This allows drivers and back-office personnel to focus on other essential tasks. Integrating ELDs with fleet management software can optimize various operational areas.
Reduce Fleet Costs
ELDs stand to help trucking companies reduce fleet costs. The devices support more efficient routing, leading to savings on fuel costs. Features like idle-time trackers help fuel management and reduce the fleet’s environmental impact.

FOR COMPREHENSIVE FLEET
MANAGEMENT SOLUTIONS
Expedite Inspections
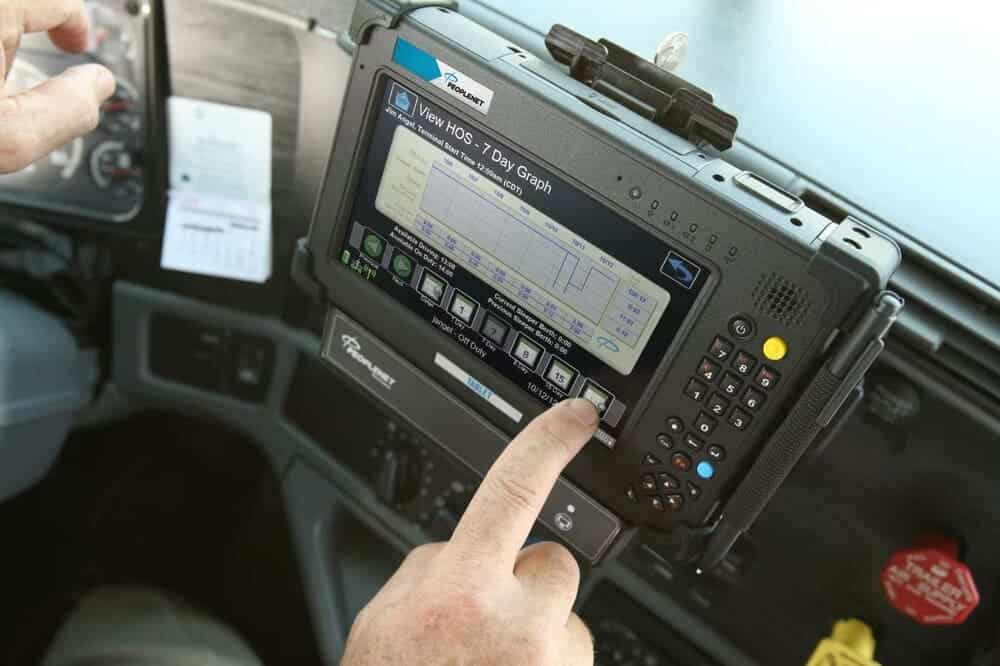
ELDs make inspections faster because drivers can easily show standardized data to safety officials when asked. Drivers can easily access graphical representations of driving duty status and detailed daily logs on a screen display or through printouts with the ELD system.
How ELD Works And Its Impact on Drivers and Fleet Management
ELD is a device that connects to a vehicle’s onboard diagnostics (OBD) port and directly extracts data from the engine. This data includes whether the engine is running, fuel consumption and the distance traveled. These devices have a built-in GPS tracker that uses global satellites to determine your vehicle’s precise location.
Top-notch ELD devices offer real-time location information, which stands to provide live-to-the-second updates on the vehicle’s whereabouts instead of “breadcrumb” location data updated every few minutes. These advanced Electronic Logging Devices have gyroscopes and accelerometers built-in. These sensors allow them to detect movement and keep track of safety-related events, such as abrupt braking or sharp turning.
Besides gathering data, ELDs can continuously transmit information to fleet managers in the back office and provide data on demand during roadside inspections to the Department of Transportation (DOT).
Compliance Requirements and Regulations for ELD Usage
Understanding the ELD rule and compliance requirements is crucial for commercial drivers to ensure their adherence to the regulations.

ELD Mandate Requirements
The ELD mandate primarily encourages the adoption of electronic logging devices among drivers who monitor their HOS. As part of this rule, drivers must replace traditional paper-based logs with electronic versions.
In addition to the core ELD adoption, the mandate introduces several specific requirements aimed at improving safety standards for commercial drivers and all road users:
-
- Certification and Registration: All ELDs must be registered with the Federal Motor Carrier Safety Administration (FMCSA).
-
- User Documentation: Commercial motor vehicles must carry user documentation, including manuals detailing the proper use of the logging devices. The documentation should also include instruction sheets outlining malfunction reporting procedures, instructions for data transfer methods, and at least eight days’ worth of blank RODS graph grids.
-
- Harassment Protection: Drivers are protected from harassment through data recorded by logging devices or fleet management systems. If drivers believe they have been harassed, they can file official complaints for recourse.
-
- Supporting Documents: You need supporting documents to make verification of on-duty, not driving time (ODND).
ELD Compliance
Complying with ELD regulations can pose challenges for businesses, especially for those accustomed to using electronic devices. Compliance means that most commercial vehicles traveling more than 100 miles need to use approved ELDs to keep track of their driving time. In general, drivers of commercial motor vehicles (CMVs) fall under this rule.
Conclusion
The ELD mandate has expedited a shift towards electronic monitoring, causing significant disruption in the trucking sector. Though it has yet to alter the established work patterns for commercial drivers, it has amplified the impact of HOS laws, leading to a more stringent environment for driving logistics.
If you still need clarification about ELD or are still determining whether the device you use is FMCSA certified, contact us today.
Sign up for Exclusive Trucking Tips
Test







